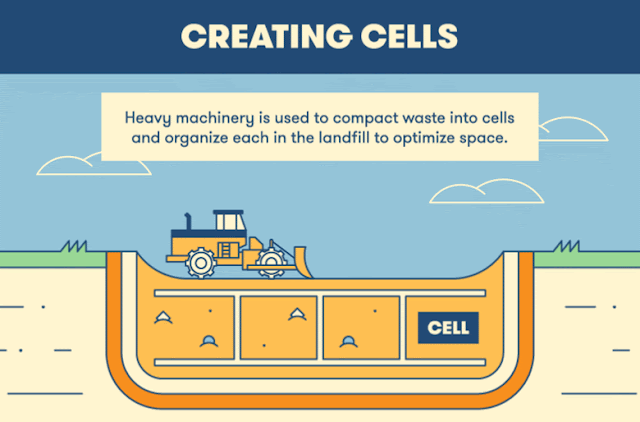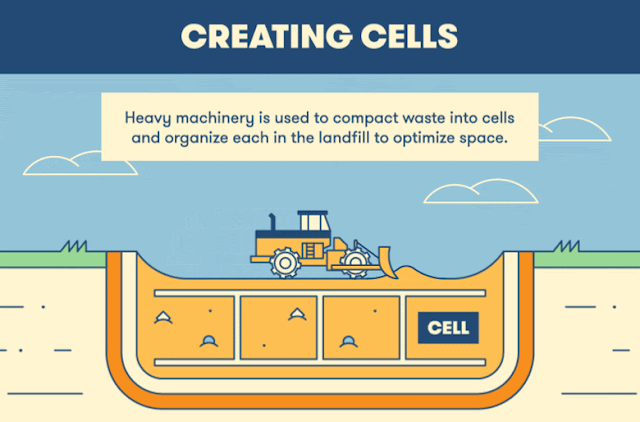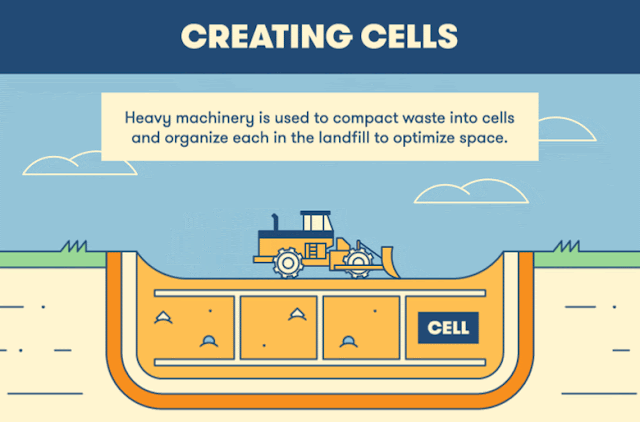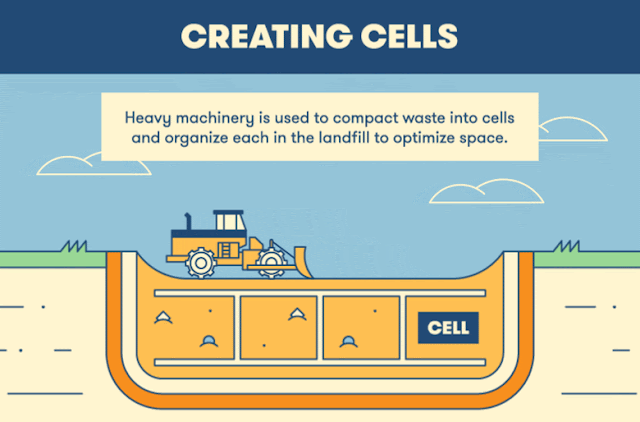
Potable water is one type of drinking water.
The norms are follows;
1.) It should be sparking clear and odour.
2.) It should be pleasant in taste.
3.) It should be perfectly cool.
4.) It's turbidity should not exceed 10 ppm( parts per million).
5.) It should be reasonable soft.
6.) It total dissolve solid should be less than 500 ppm.
7.) It should be free from Objectionable dissolve gases like Hydrogen sulfide H2S.
8.) It should be free from objectionable mineral such as lead, arsenic, chromium.
9.) It's pH should be about 8.
10.) It should be free from disease producing micro-organisms.